€24.48 – €34.04
Key Features
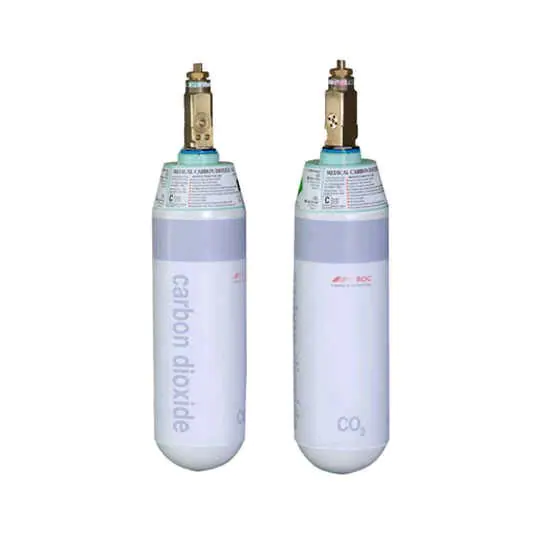
BOC Healthcare provides an extensive range of specialist medical gases and equipment for healthcare professionals and Medical Carbon Dioxide Cylinder Compressed Gas is offered in a variety of cylinder packages designed to meet customer usage levels.
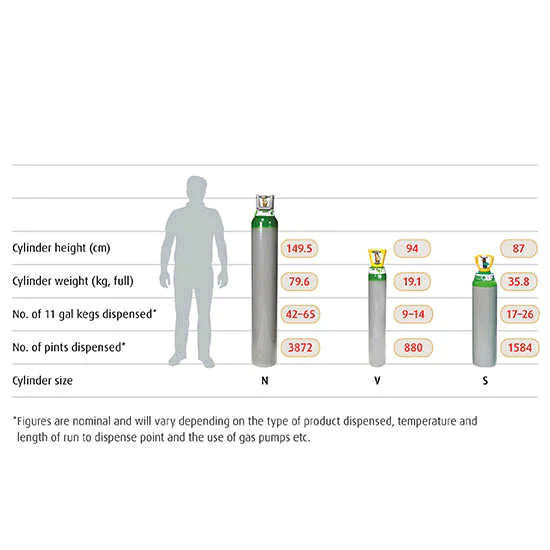
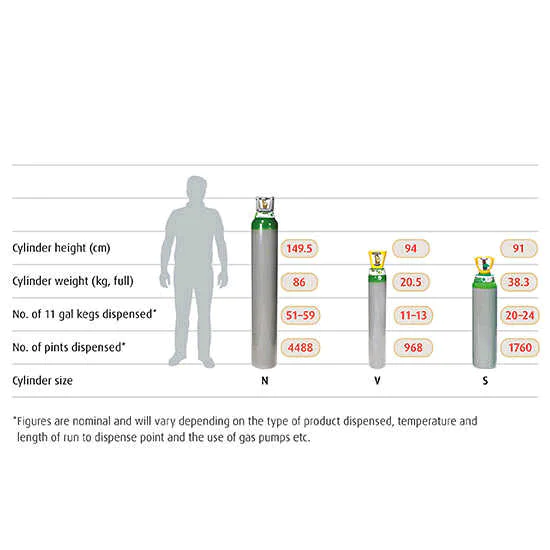
This ranges from the C 450-liter gas cylinder through to the VF option, which offers 3600 litres of carbon dioxide. Please refer to the cylinder guide on this page for all cylinder sizes.
BOC Healthcare can also provide a range of medical cylinder trolley and storage solutions.
Medical Carbon Dioxide Cylinder Compressed gas is commonly used as an insufflation gas for minimally invasive surgery (laparoscopy, endoscopy, and arthroscopy) and to enlarge and stabilize body cavities to provide better visibility of the surgical area.
It may also be used in cryotherapy, where temperatures of -76° C, can be achieved as well as respiratory stimulation during and after anaesthesia.
- Provides respiratory stimulation during and after anaesthesia
- Also used in Cryotherapy, where temperatures of -76°C, can be achieved. Using this technique body cells are destroyed by the process of crystallisation. This may include the removal of wart, moles and skin tags.
- Wide range of cylinder packages to suit customer usage levels
- 3600 litres VF Option for large on-site supply
- 450 litres C cylinder for lighter usage
- Full range of ancillary equipment for storage and mobility is available
may develop with malaise, pallor, headache and occasional nausea and vomiting, probably due to the
metabolic disturbances as a result of breathing volatile acid.
As the inspired concentration rises, these effects become exaggerated in proportion to the concentration.
At around 8-9% dizziness may develop, and at 10% some subjects become unconscious. Most people will
become unconscious at 12.5% and all subjects lose consciousness within 1-2 minutes at 20%. When the
concentration is raised to 30% consciousness is lost rapidly, and the blood pressure may rise to 27 kPa.
(200mm Hg) or higher and there is intense vasoconstriction, a reduction in heart rate to 40-50 heats per
minute and ECG changes. All anaesthetic agents reduce these responses to carbon dioxide.
When inhaled, carbon dioxide is rapidly distributed throughout the body. Physiologically, it regulates the
rate and depth of breathing and normally there is a constant tension of 5 kpa (40mm Hg) in arterial blood.
The concentration of carbon dioxide in the plasma is three times greater than that in red blood cells. The
gas is carried partly in solution (2.4 – 2.7 vol %),but mostly either as bicarbonate (42.9 – 46.7 vol%), or as
carbamino compound (3.0 – 3.7 vol%).
The relative quantities in solution and as bicarbonate regulate the reaction of the blood and buffer changes
in pH produced by stronger organic acids.
Carbon dioxide produced by metabolism plays an integral part in the supply of oxygen to the tissues, since
the amount released by haemoglobin at any given oxygen tension is directly related to carbon dioxide
tension in the blood. This, in turn, is governed by tissue activity in the concentration inhaled. Thus the rate at
which oxygen is given up to the tissues is increased when the carbon dioxide tension is raised.
When a patient becomes apneic, carbon dioxide produced in the tissues accumulates in blood at a rate of
about 0.7kpa (5mm Hg) per minute.
| Cylinder Size | C (450 litres), E (1800 litres), LF (3600 litres), VF (3600 litres) |
|---|
Be the first to review “Medical Carbon Dioxide Cylinder Compressed Gas” Cancel reply
Related products
Carbon Dioxide













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.